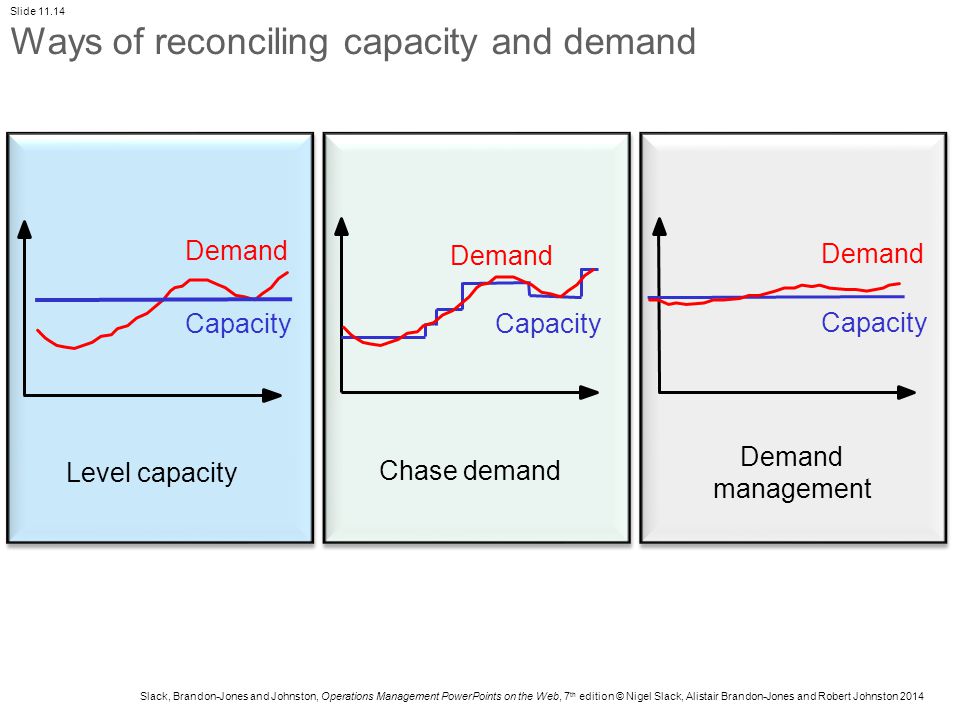
Chase demand strategy can be defined as a strategy where the changes are made to the output according to the demand Here, the changes are in terms of increasing or decreasing the output in line with the rising or falling demand It involves matching the demand by hiring or firing the workers or by controlling the level of production and using Types of Capacity Planning Strategies 1 LEAD STRATEGY The Lead Strategy involves an upfront investment in more capacity that is needed and is one of the 2 LAG STRATEGY The Lag Strategy is much more conservative than the Lead Strategy as it waits until the current 3 MATCH STRATEGY The The chase strategy sets production equal to forecasted demand Many service organizations such as schools, hospitality businesses and hospitals, use the chase strategy The level strategy is mainly focused on maintaining a constant output rate This strategy is mainly adopted by manufacturing companies

Ie 3265 Production Operations Management Slide Series
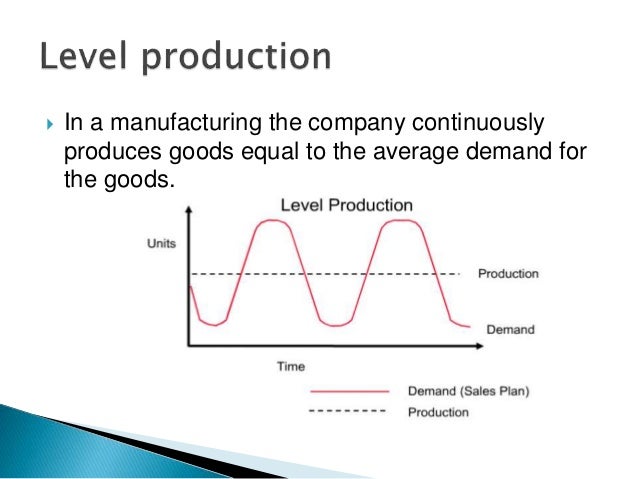
Level capacity strategy
Level capacity strategy-Diversification can occur either at the businessunit level or at the corporate level of economies of scale, economies of scope, new locations, new technology, or some other form of increased competitive capacity Mergers and Acquisitions Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are aspects of corporate strategy, corporate finance, and managementCapacity Decisions are Strategic 1 Capacity decisions have a real impact on the ability of the organizationto meet future demands for products and services 2 Capacity decisions affect operating costs 3 Capacity is usually a major determinant of initial cost Typically, the greater the capacity of a productive unit, the greater its cost 4




Capacity Strategy Pdf Economies Of Scale Strategic Management
Develop the Local Capacity Strategy , 33 II UNDP HeadquartersManaged Programs with a Focus on the Local Level, 36 IIIUNDP's Environment & Energy Group's (EEG) Work at the Local Level, 37 IV UNDP Mandate to Work at the Local Level , 39 V How UNDP's Practices and Teams Can Advance the Local Capacity Strategy, 40 VI An approach to aggregate planning that attempts to match supply and output with fluctuating demand Depending on the product or service involved, the approach can incur costs by the ineffective use of capacity at periods of low demand, by the need to recruit or lay off staff, by learningcurve effects, and by a possible loss of quality The advantages include low storageBusiness unit level strategy This level focuses on how you're going to compete
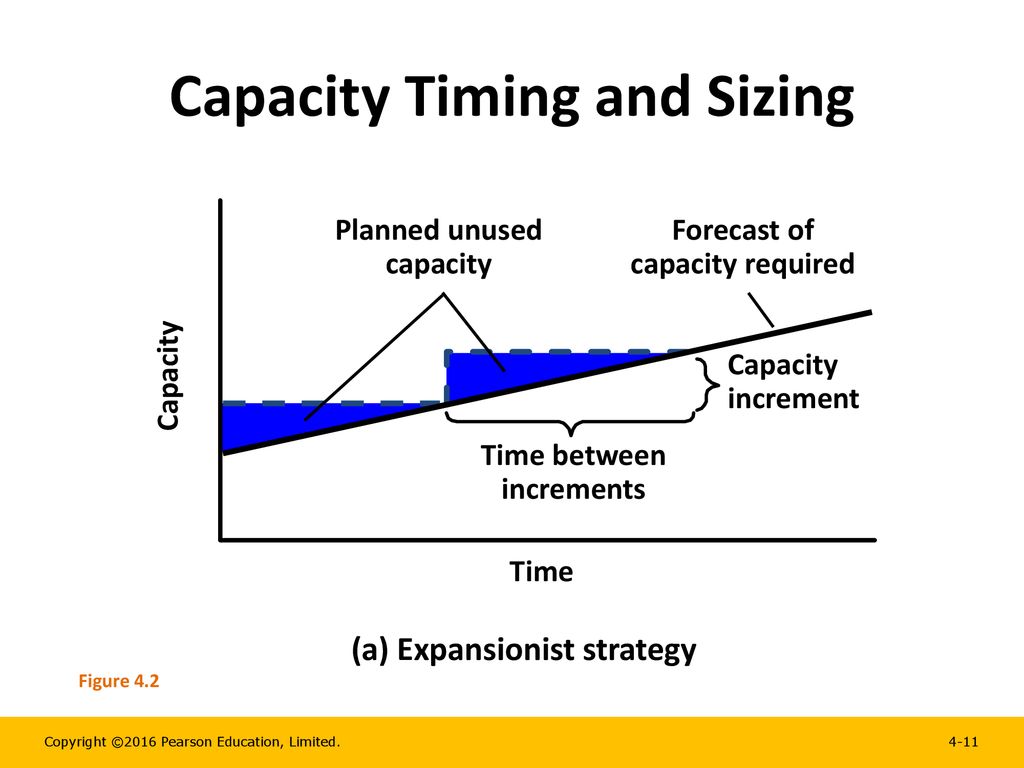
The overall objective of strategic capacity planning is to reach an optimal level where production capabilities meet demand Capacity needs include equipment, space, and employee skills If production capabilities are not meeting demand, it will result in higher costs, strains on resources, and possible customer lossIn this rundown of the juggling feat service managers perform, the author discusses the two basic strategies—"chase demand" and "level capacity"—available to most service companies Lead Strategy An upfront investment in more capacity that you need This can be done when capacity is inexpensive or difficult to obtain For example, a new vineyard anticipates using less than 10 acres of land in its first 5 years but purchases 100 acres of land as a long term investment in the business
In order to use the level capacity strategy, variations in demand are met by A varying output during regular time without changing employment levels B varying output during regular time by changing employment levels C varying output by changing overtime levels D using combination of inventories, overtime, part time, and back ordersThe level capacity strategy involves maintaining stable workforce level and output rates over the planning horizon This allows the firm to maintain inventory levels of finished products higher than expected in situations of low demand variability As demand increases above the steady output rate, the firm can continue to maintain The article addresses the estimation of capacity for an equity fund that forms portfolios based on a given investment strategy It fits within three strands of literature i) theoretical models of optimal trading or portfolio construction under alpha erosion and trade frictions;




7 Reasons For Supply Chain Planning Software Supply Chain 24 7




Chapter 5 Strategic Capacity Planning For Products And
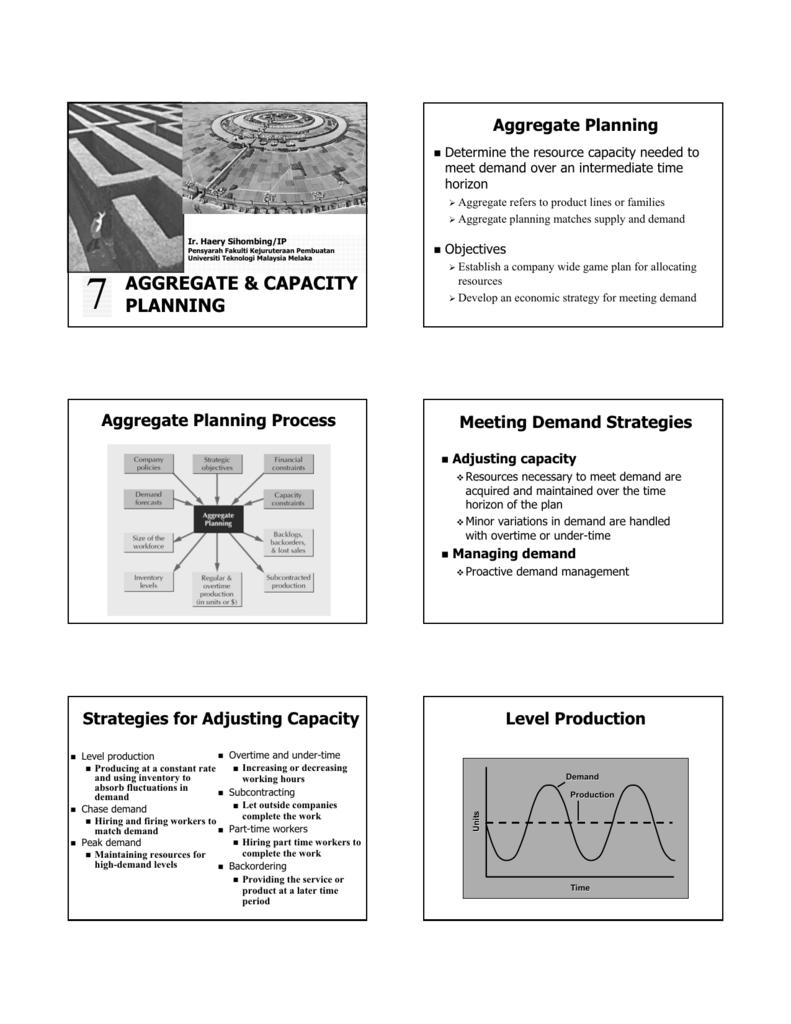
Level Capacity Strategy 1 The utilization of operational resources throughout the year 2 Efficient level of production can be maintained 3 Decreases the marginal costA body of theory based on applied statistics that help managers evaluate the relationship between capacity decisions and important performance issues such as waiting times and line lengths priority rules rules for determining which customer, job, or products isAggregate capacity is the total amount of capacity required or available to carry out a function It also tells about the 3 best strategies for aggregate planningThey are level strategy, Chase strategy and hybrid strategy Aggregate planning is the process of developing, reviewing, analyzing, and maintaining aggregate plans




The Emergence Of Absorptive Capacity Through Micro Macro Level Interactions Sciencedirect




Optimal Capacity And Price Levels For Different Capacity Investment Download Scientific Diagram
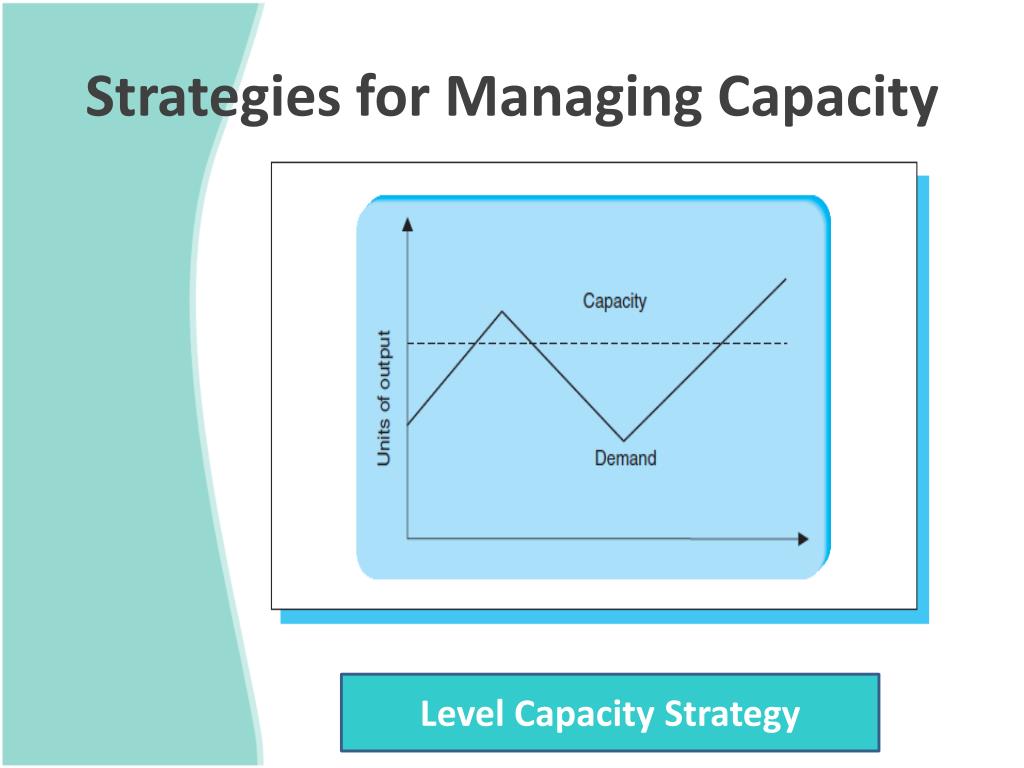
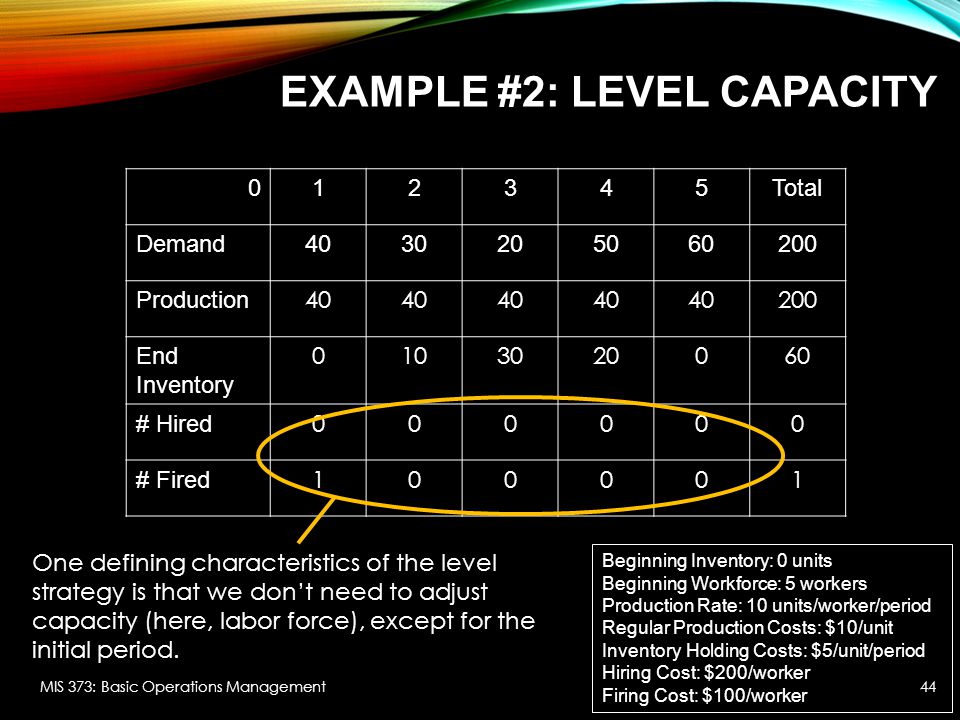
A level strategy allows a firm to maintain a constant level of output and still meet demand This is desirable from an employee relations standpointThe advantages of the Level capacity strategy a Employment of operational resources at all times b Efficient production stages can be held at a constant rate c Lowers unit cost for examples, mass production or manufacturing of uniform productsProblem 131 level strategy allowing backorders Calculate the production rate and workforce level Develop the plan, calculate the costs, and evaluate the strategy Problem 1334 chase strategy 3) Calculate the production rate and workforce levels 4) Develop the plan, calculate the costs, and evaluate the strategy




Solved Level Capacity Strategy Is Considered As A Proactive Chegg Com




Solved When Using A Level Capacity Strategy Or Level Chegg Com
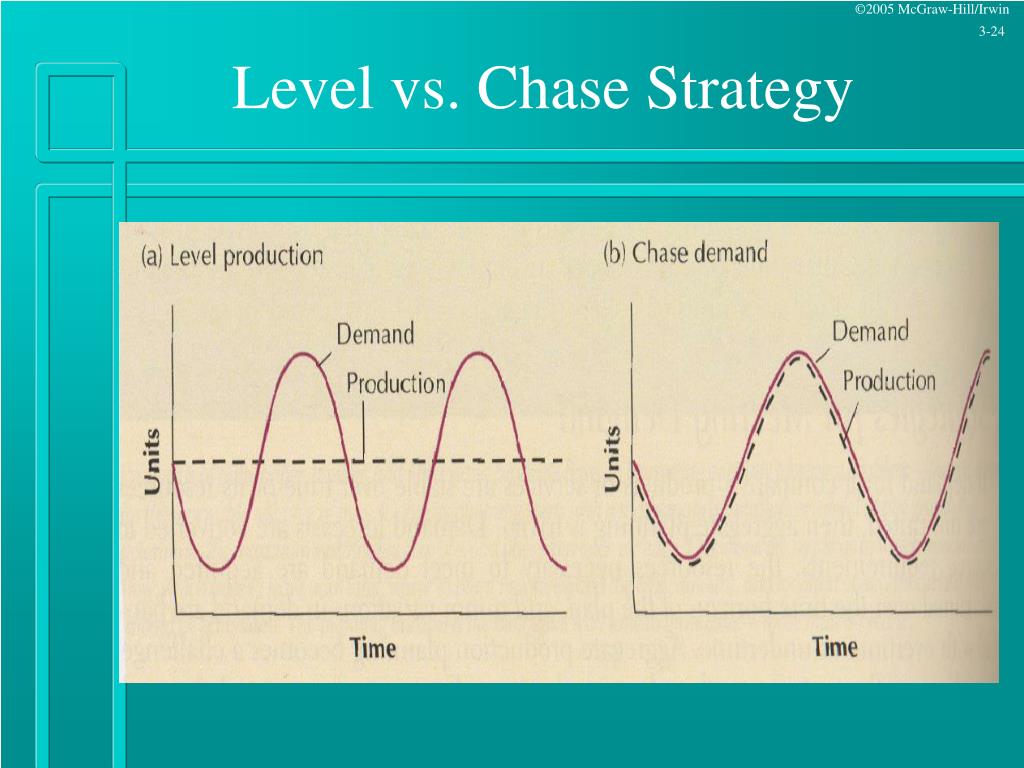
It looks at the availability of those resources at the skill set/team level Then it facilitates the decisionmaking process to hire resources or defer/approve/cancel projects Capacity planning is about supply and demand With the level strategy, production remains at a constant level in spite of demand variations In companies that produce to stock, this means that finished goods inventory levels will grow during low demand periods and decrease during high Capacity planning is a strategic process whereby a company determines what level of capacity it will need to satisfy the level of demand




Pm10 Mock Exam Flashcards Quizlet




Aggregate Capacity Planning Pdf Free Download
At one extreme is a levelcapacity strategy, in which the firm designs its systems to provide a constant level of capacity and absorbs the costs when demand is far above or far below that level At the other extreme is the strategy to meet current needs A given firm's optimal level of flexibility to match capacity to demand will fall Capacity planning is defined as a method to gauge the production capacity needed to meet the changing product demands of an organization Two terms of design capacity and effective capacity are used extensively in the context of capacity planning The first is the maximum work that is completed in a specific period by an organization, and the latter is theIi) empirical estimates of capacity for specific equity strategies;




Demand And Capacity Planning In The Emergency Department How To Do It Emergency Medicine Journal




Saesipjosuz8q 印刷可能 Level Capacity Strategy Pdf 1303 Level Capacity Strategy Pdf
When it comes to scheduling your labor force, there are two primary ways to schedule The first is called level scheduling, where you try and maintain a steady workforce with a steady schedule The second is the chase strategy, where you maintain a level workforce and increase your workforce as demand increasesThis A level Business revision tutorial investigates the concept of capacity utilisation in a business and the strategies managers may use if capacity utilis The three levels of strategy are Corporate level strategy This level answers the foundational question of what you want to achieve Is it growth, stability, or retrenchment?



Planning Capacity Chapter Ppt Download



Water Free Full Text Unpacking Water Governance A Framework For Practitioners Html
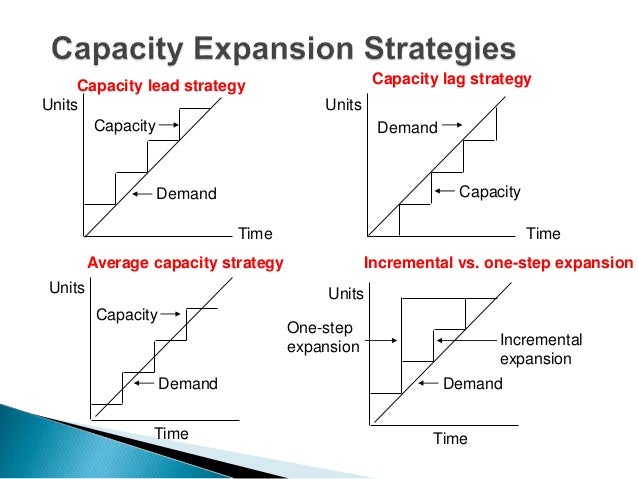
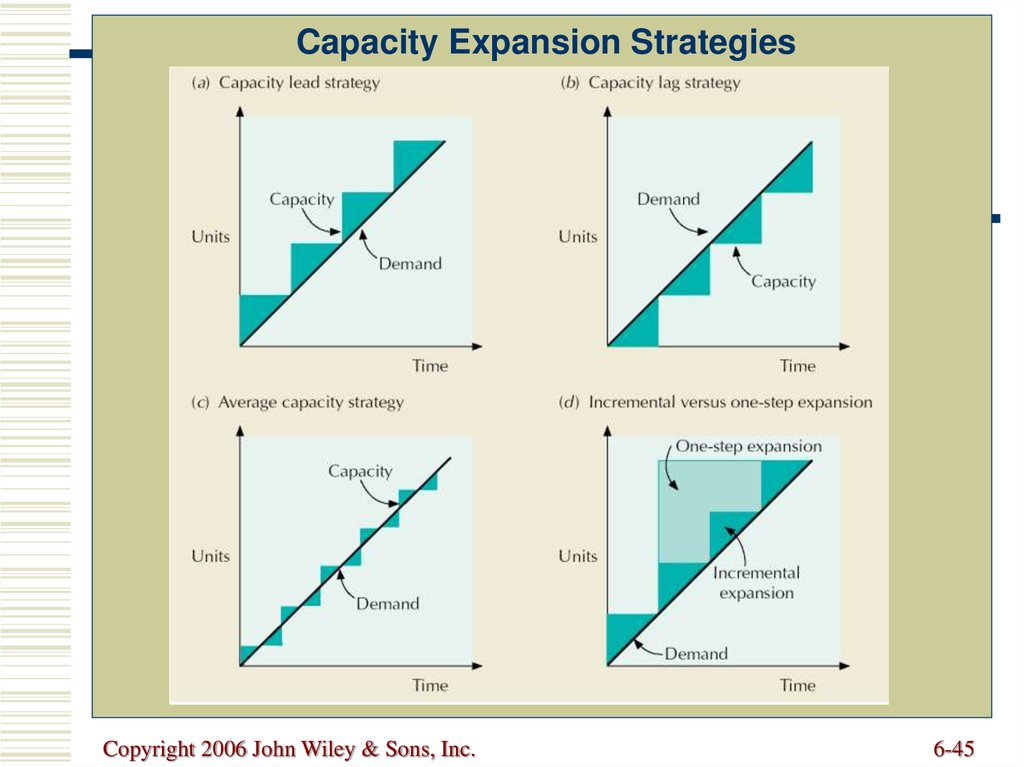
Strategies The broad classes of capacity planning are lead strategy, lag strategy, match strategy, and adjustment strategy Lead strategy is adding capacity in anticipation of an increase in demand Lead strategy is an aggressive strategy with the goal of luring customers away from the company's competitors by improving the service level and reducing lead time 3 Types of Capacity Management John Spacey, Capacity management is the process of planning the resources required to meet business demands This includes capacity forecasting, planning, monitoring and performance analysis This can happen at three levels in an organization Organization and systemslevel measurement strategies such as those used to operationalize Lang's system capacity and readiness offer an example Working toward a more complete body of evidence showcasing outcomes on multiple levels would support more informed decision making around capacitybuilding interventions and how best to deliver them




Ch 11 Aggregate Planning And Master Scheduling Flashcards Quizlet




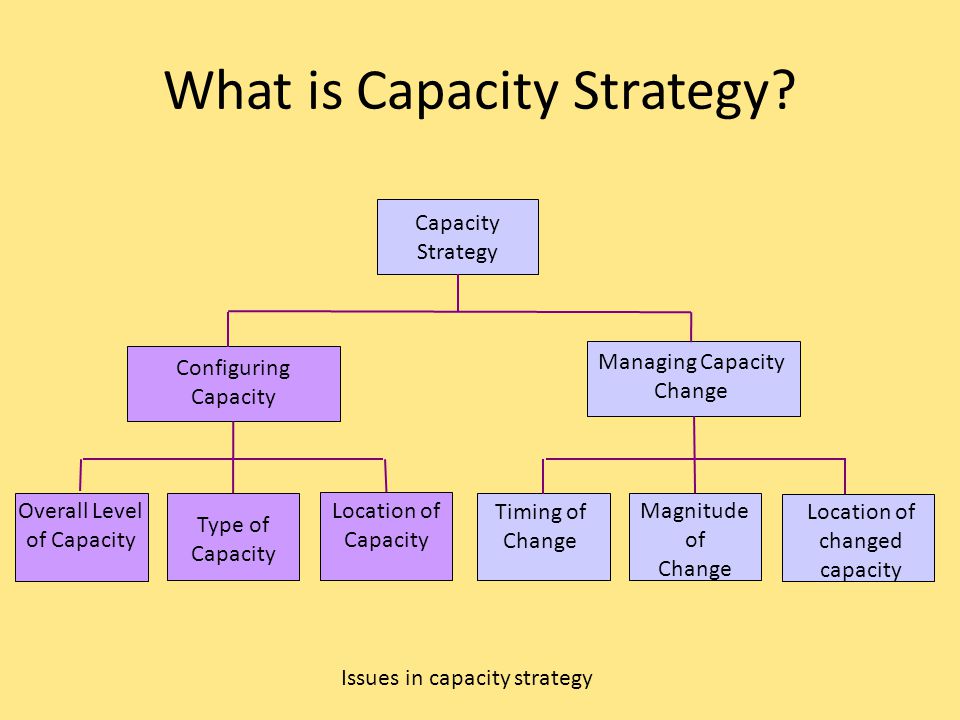
4 Capacity Strategy
This revision video provides an overview of the concept of capacity, capacity utilisation and some of the issues facing businesses operating at low or high u 3 Hybrid strategy for an aggregate planning As the name indicates, the Hybrid strategy is an integration of both level and chase strategies to get a better result It maintains a sufficient balance between stock level, recruiting, termination and production rate In the hybrid strategy of aggregate planning, the organizations build upCapacity development responsibilities under one umbrella to tackle some of the systemic in order capacity constraints and address new capacity emanating from the new programme elements needs This CD Strategy provides a framework to coordinate and implement CD in a systematic and efficient manner




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute



2
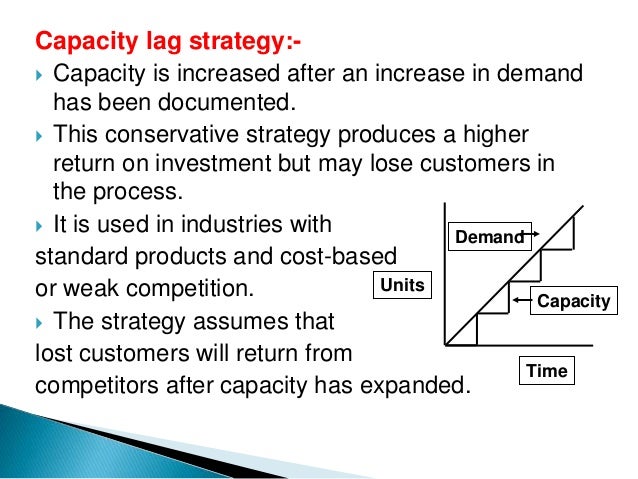
Each method is based on reacting to or planning for market fluctuations and changing levels of demand These capacity planning strategies are match, lag, lead, and adjustment Match Matching involves monitoring the market for demand increases and decreases on a regular basisView the full answer Transcribed image text question in order to use the level capacity strategy, variation in demand are met by select one a using some combination of inventories, overtime, part time, subcontracting and back orders b varying output by changing overtime levels C varying output during regular time without changing employment levels d price adjustments e varying Lag strategy is planning to have enough resources to meet true demand (not projected) Lag strategy is a conservative method of capacity planning that ensures your costs are as low as possible The potential downside to this strategy is that it can create a lag in the delivery of products or services to customers, which is where the name comes from



Capacity Management




Impact Of The Level Of Reactive Capacity On The Protability Of Download Scientific Diagram
Below are some of the most popular capacity management strategies #1 – Lag Strategy Using this conservative approach, a manager determines the capacity and then waits until there is an actual steady increase in demand Then, the manager raises the production capabilities to a level to satiate the current market needChase Capacity Management Opposite to the level capacity management is the chase capacity, " organisations could decide to match capacity and demand by altering the availability of resources This might be achieved by employing more people when it is busy and adopting strategies such as overtime and additional shiftsExplain about the level capacity strategy Level capacity strategy The organisation produces or manufactures at a constant rate of output avoiding any changes or fluctuations within customer demand levels This frequently implies stockpiling or higher holdings of inventory while customer demand levels reduce




Monitoring And Evaluation Of Brazilian South South And Trilateral Cooperation Sstc On Capacity Development And Social Protection Learnings From The Field Socialprotection Org



Ppt Chapter 3 Aggregate Planning Steven Nahmias Powerpoint Presentation Id
Level capacity strategy The organisation manufactures or produces at a constant rate of output ignoring any changes or fluctuations in customer demand levels This often means stockpiling or higher holdings of inventory when customer demand levels fall




Production Planning Control Chapter 2 Aggregate Planning Master Production Scheduling Chapter2 1 Pdf Free Download




Capacity Management Bus32 Studocu



1



Capacity Management




Ppt Chapter 3 Aggregate Planning Steven Nahmias Powerpoint Presentation Id 9337




Multi Level Model For Building Capacity For A National Quality Download Scientific Diagram




11 Managing Resources Flashcards Quizlet




Requirement Docx Requirement A Level Capacity Strategy Difficult For A Firm Wishing To Adopt A Jit Philosophy About Level Capacity Level Capacity Course Hero



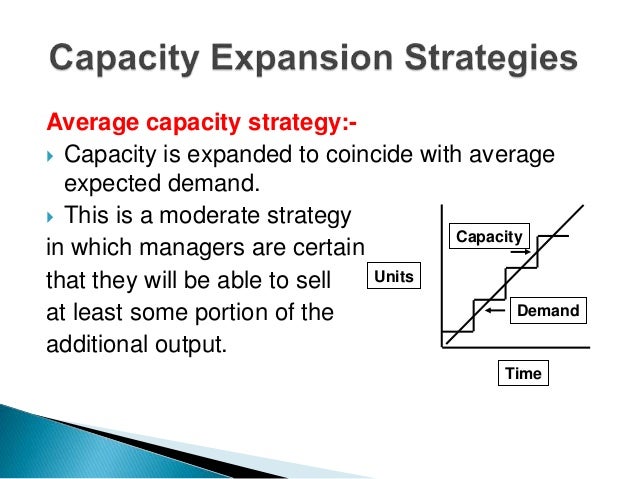
Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download




Categorization Of Capacity Planning By The Planning Horizon Download Table




Pdf Lean Capacity Planning Planning For Maximising Customer Value Semantic Scholar




Lecture 7 Production Planning System Revisited Books Introduction




Aggregate Planning Chapter 11 Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Demand And Capacity Management Options Adapted From Fitzsimmons And Download Scientific Diagram




Ie 3265 Production Operations Management Slide Series




Long Term Capacity Management Linking The Perspectives From Manufacturing Strategy And Sales And Operations Planning Sciencedirect




Capacity Strategy Pdf Economies Of Scale Strategic Management




Capacity Management Strategies And Service Quality In Petroleum Distribution Firms In Kenya Pdf Free Download




Strategic Capacity Planning Capacity Utilization




Chapter 13 Production Planning Supplemental Slides 1 Overview




Capacity Management Strategies And Operational Efficiency In The Energy Sector In Kenya Semantic Scholar




Aggregate Planning 2 Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning Intermediaterange



1




Achieving High Performance Low Cost Logistics Netherlands Kearney
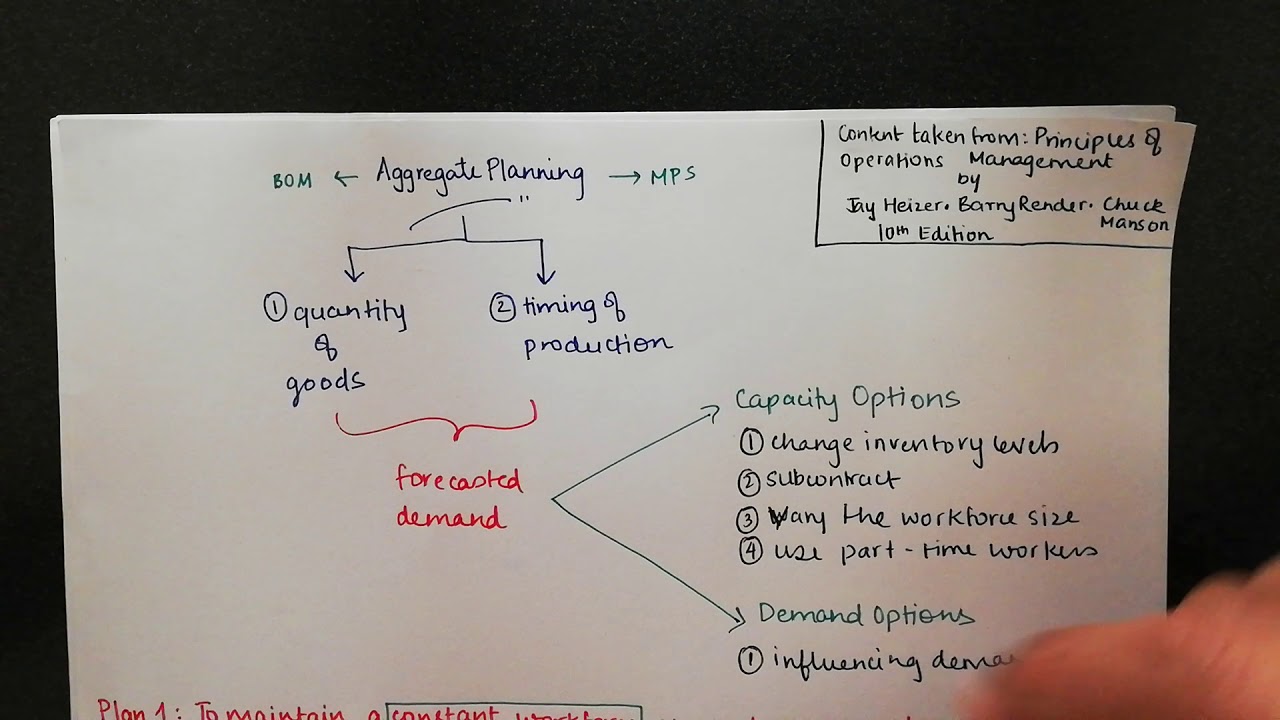



Introduction To Aggregate Planning And The 3 Plans Level And Chase Strategy Included Youtube




Entries For Thursday 25 October 07 Sergio S Blog
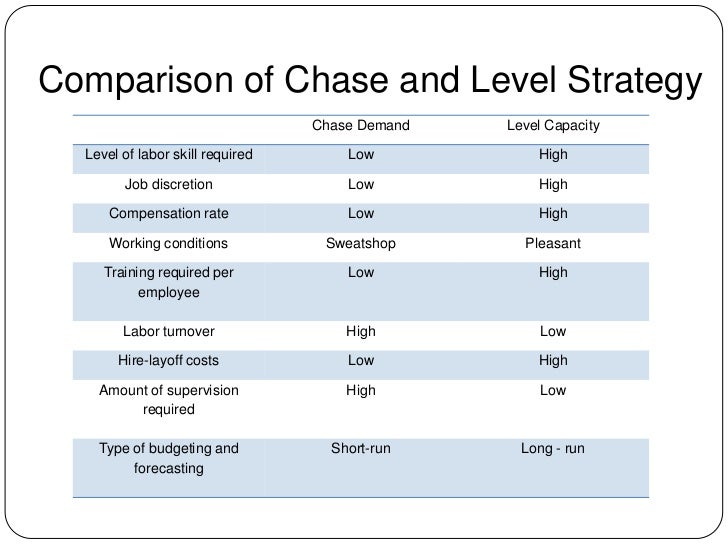



Aggregate Planning Report



M Dc Operations Strategy



Capacity Management



1



Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute




Multilevel Strategies To Build Support Continuous Organizational Download Scientific Diagram




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute



Chapter 11 Capacity Management Ppt Video Online Download




Sales And Operations Planning Aggregate Planning Production Planning



Ppt Capacity And Scheduling Management Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




How Is Yield Management Implemented In Airline Industry Ayat Saleh




Jones Robinson Operations Management All Operations Need To Know The Likely Customer Demand For Their Goods Or Services On Any Given Day Week Or Year Ppt Download




Capacity Planning Organization System Examples Definition System Long Term Capacity Planning




Pdf Using Expanded Real Options Analysis To Evaluate Capacity Expansion Decisions Under Uncertainty In The Construction Material Industry Semantic Scholar




Aggregate Planning



Overcoming Obstacles Of Supply Chain Synchronization Gexso




12 1 Aggregate Planning Operations Management William J




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Lecture 15 Chapter 11 Capacity Planning And Control Introduction Studocu



Aggregate Capacity Planning Sihombing15 S Haery Sihombing




Bakery S Cif Introduction To Capacity And Facilities



Capacity Management




Solved Question 26 Level Capacity Strategy Is Considered As Chegg Com




Basic Strategies Level Capacity Strategy Chase Demand Strategy Ppt Download




Pdf Long Term Capacity Management Linking The Perspectives From Manufacturing Strategy And Sales And Operations Planning Semantic Scholar



1




Operations Management Lesson 8 Flashcards Quizlet




Slides For Chapter 10 Strategic Capacity Honda On July 18 Announced Two New Plants In Argentina Honda Will Spend 100 Million On A New Compact Car Ppt Download




Ppt Planning Demand And Supply In A Supply Chain Powerpoint Presentation Id




Strategic R D Portfolio Management Vs Operational Capacity Planning A Tale Of Two Disciplines Enrich Consulting




Ppt Chapter 11 Strategic Capacity Management Powerpoint Presentation Id 9169




Ppt Strategic Capacity Planning Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Aggregate Planning




Hp Capacity And Service Level Mgmt For Sap R 3 08 01 Indd




Capacity Strategy Some Factors Influencing The Overall Level Of Capacity Forecast Level Of Demand Consequences Of Over Under Supply Availability Of Ppt Download




Consultation On Gnc Draft Capacity Building Strategy Nutrition Cluster



2




Long Rang Capacity Planning Ppt Download




Optimal Capacity And Price Levels For Different Capacity Investment Download Scientific Diagram




The Future Of Strategic Operations Management




Style Linear Single 5 Piece Powerpoint Presentation Diagram Infographic Slide Presentation Powerpoint Templates Ppt Slide Templates Presentation Slides Design Idea




Aggregate Planning Ppt Slides




Strategy Under Uncertainty




Stevenson 14e Ch11writing Pdf




Aggregate Planning Planning Horizon Aggregate Planning Intermediate Range




Covid 19 Decontamination And Reuse Of Filtering Facepiece Respirators Cdc
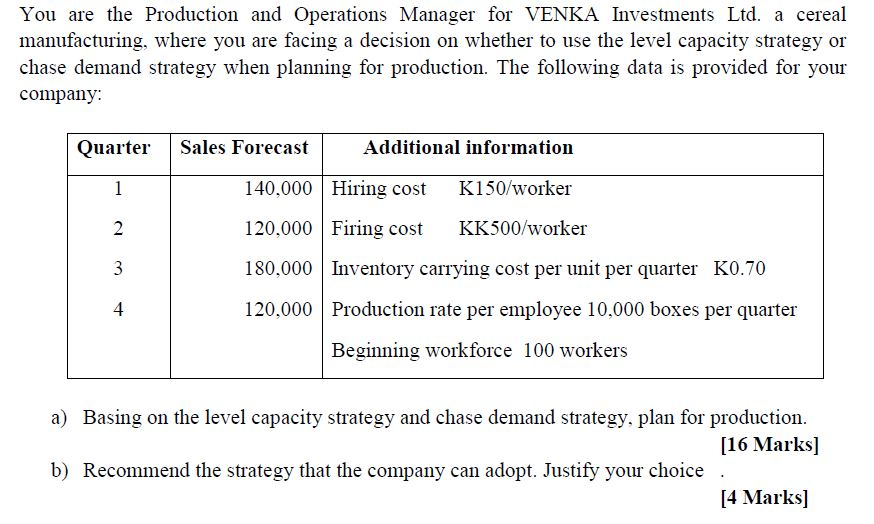



You Are The Production And Operations Manager For Chegg Com




Capacity Management Service Quality And Customer Satisfaction In Information Technology Service Companies In Nairobi Kenya Semantic Scholar




Capacity And Aggregate Planning Aggregate Planning The Process



Processes Technology And Capacity Prezentaciya Onlajn




Operations Management Daniel S Blog



Aggregate Planning Chapter 11 Mis 373 Basic Operations Management Ppt Download




Capacity Planning Kaizen Chronicles



2




Demand And Capacity Management Options Adapted From Fitzsimmons And Download Scientific Diagram
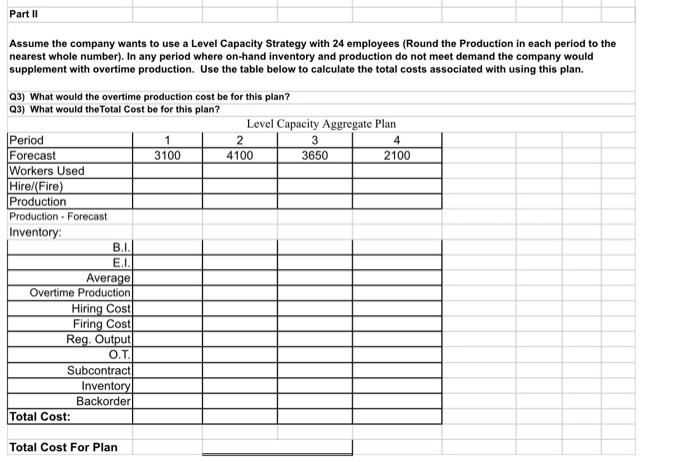



Solved Part Ii Assume The Company Wants To Use A Level Chegg Com
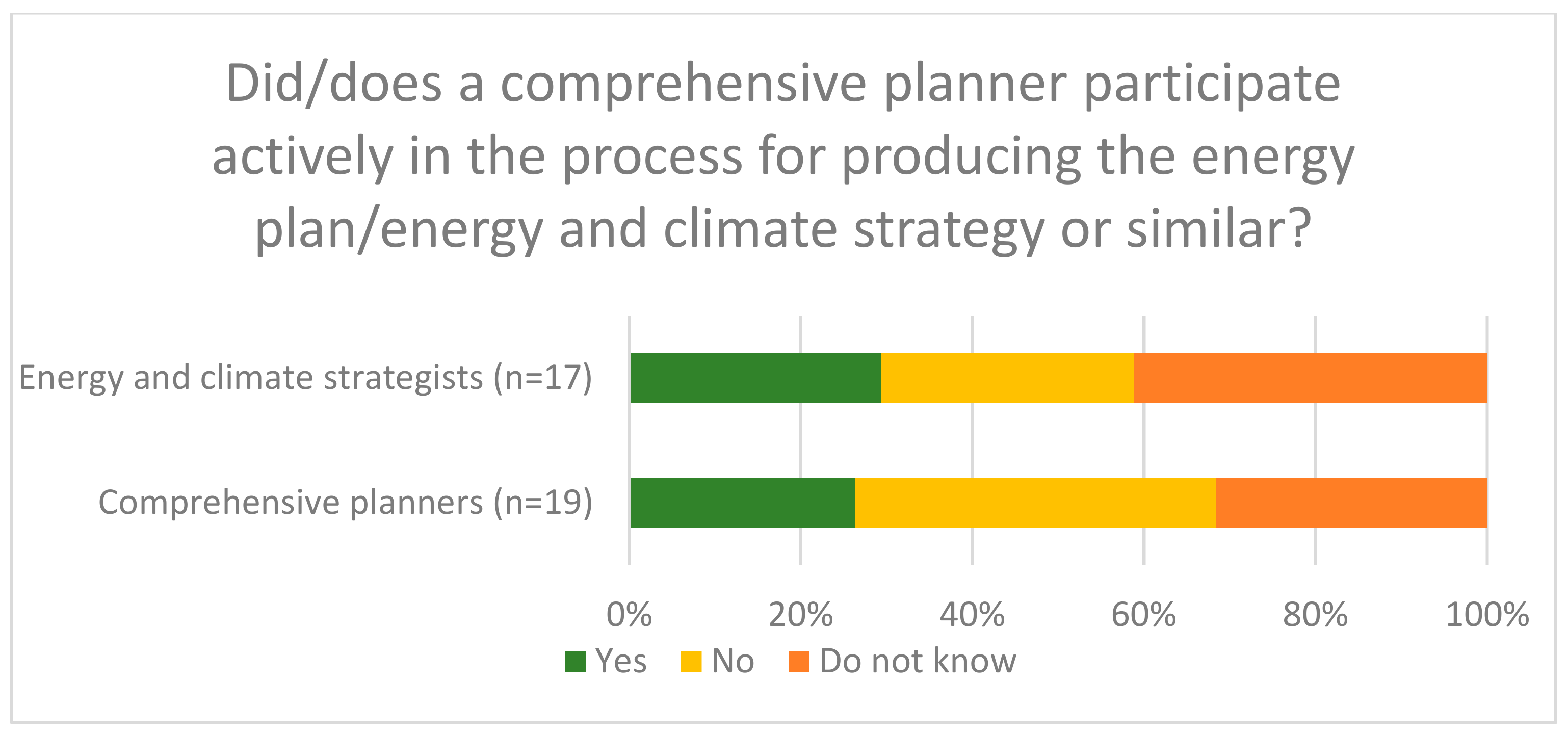



Sustainability Free Full Text Building Institutional Capacity To Plan For Climate Neutrality The Role Of Local Co Operation And Inter Municipal Networks At The Regional Level



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿